When picking out an HVAC system, it’s increasingly popular to prioritize energy efficiency — not only is it good for the environment, but it saves you money! Deciding on the most energy efficient HVAC system depends on your home and situation, but across the board they will lower utility cost and fossil fuel usage. To help you decide the best system for you, we’ve highlighted the most energy efficient air conditioners and heating systems.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
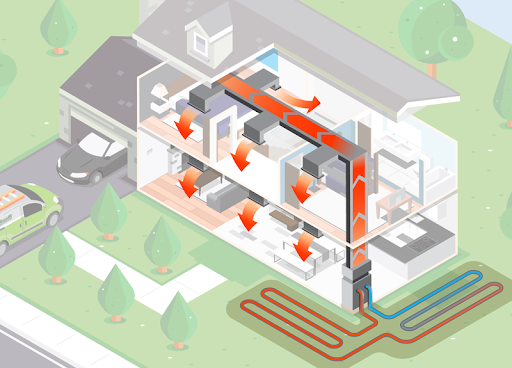
Geothermal heat pumps are one of the most energy efficient home heating and cooling systems — yes, that’s right, they aren’t just for heat, but also cool. Instead of using energy to create hot or cool air in your home, geothermal systems use the nearly constant temperature of the earth via small pipes buried underground referred to as a “ground loop.” Above ground, the only visible part of the unit is a single indoor heat pump that connects the home to the underground loops. The indoor unit can connect to either ductwork or a radiant heating system within the home.
In addition to their efficiency, geothermal heat pumps typically last 10 years longer than traditional HVAC systems and require minimal maintenance since the system is underground. However, in order to install a geothermal heat pump, a home needs ample property space to drill into the ground and place the loops. There are two different kinds of heat pumps to install: closed loops and open loops. For our geothermal installations, we install closed loop systems.
WHAT IS A CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM?
A ground loop is a series of pipes buried underground that circulates a heat-absorbing carrier fluid. These loops are buried at a depth where temperatures stay consistent year-round. Regardless of the outdoor temperature, the ground temperature of the earth maintains between 50 and 55 degrees. This difference in temperature allows the earth to act as a heat source in winter and a heat sink in summer. In winter, the fluid absorbs heat from the warmer earth and carries it into the heat pump, where it enters a heat exchanger and is used to warm your home. In summer, the process is reversed when the home’s heat is captured and released into the cooler ground, leaving your home comfortably air-conditioned.
When considering a geothermal heat pump, there are two types of closed loop systems to choose from: vertical and horizontal. The installation for each system depends on your property’s outdoor space, environment, and landscape.
VERTICAL VS HORIZONTAL CLOSED LOOP SYSTEMS
Vertical systems are installed in one or more boreholes, from 200 to 500 feet deep in the ground. Each hole is five to six inches in diameter, and if you have more than one, they’re about 20 feet apart. Since the width of the hole is smaller in size, vertical loops are ideal for homes where ground space is limited, when rock formations are very close to the surface, or retrofit applications where minimum disruption of the landscaping is desired.
In a horizontal system, holes are drilled over a wider area but are only five to six feet in the ground. The trenches are hundreds of feet long, meaning the property needs an outdoor area with ample space. In addition to yard space, the ground should also be easy to drill into to create the trenches.
ENERGY EFFICIENCY IN GEOTHERMAL HEAT PUMPS
Each system is ideal for different types of properties, but still has the same energy efficiency. Compared to other HVAC solutions, geothermal heat pumps are the most energy efficient and environmentally friendly because they rely on the unchanging ground temperature. With a constant heat source, these systems do not need oil or gas to function. Instead they use minimal electricity to cool or heat the home, making them extremely efficient.
FACTORS THAT CAN AFFECT ENERGY EFFICIENCY
While geothermal heat pumps require less work after installation, homeowners still need to monitor the system’s efficiency. Some factors that can affect efficiency include ignoring seasonal maintenance and inspection, not cleaning or replacing air filters, and having dirty coils or fans. Proper maintenance creates a sound system for heating and cooling, and also keeps your energy bills at their lowest cost.
COST SAVINGS WITH GEOTHERMAL HEAT PUMPS
With a properly maintained system, homeowners can reduce their energy bills significantly. A geothermal heat pump can save between 30% and 50% on energy bills. When combined with a solar panel or other renewable energy sources, they can also create a net zero energy home. Net zero energy homes can save even more on bills by eliminating them altogether, and homeowners can often apply for tax credits and rebates. While the initial installation cost can be high, a geothermal heat pump generally pays for itself in 10 years.
Forced Air
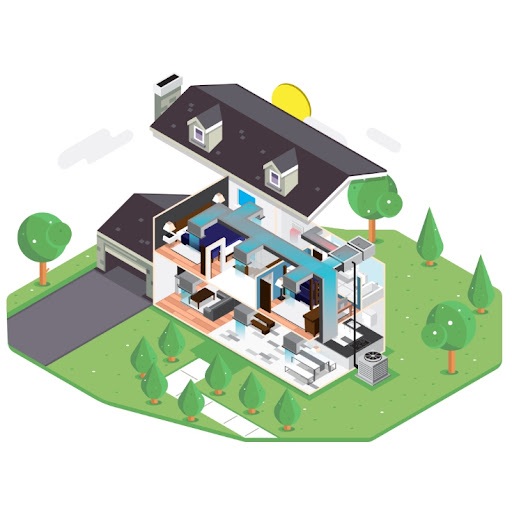

Another energy efficient way to heat and cool your home is through a forced central air system. Forced air uses ductwork in the home to distribute warm or cold air into each room. While the ducts can be used for both heating and cooling, it requires installing two separate systems for each, creating an invasive installation process. However, after the installation, forced air systems can offer a variety of ways for energy efficiency and lower utility bills.
COOLING WITH FORCED AIR
To install an air conditioner that uses forced air, homes require an outdoor condenser and an indoor air handler. The air handler is usually placed in an attic and runs ductwork throughout the home. Each home requires properly sized equipment to sufficiently cool the entire home or area. Larger or more complex homes may require multiple systems for multiple zones.
HEATING WITH FORCED AIR
To combine heating and cooling in the same ductwork, homeowners can install a furnace with an air conditioning coil and handler. The systems can either be installed at the same time, or an air conditioner can be retrofitted onto an existing heat system. A thermostat is used to determine whether heating or cooling is required.
Forced air furnaces are great for efficiency, and can have up to 98% annual fuel utilization efficiency, or AFUE. Efficiency ratings determine what percent of fuel is used to heat your home. With a 98% system, only 2% of fuel goes to waste.
ENERGY EFFICIENCY IN FORCED AIR SYSTEMS
The efficiency of a forced air system is determined by the type of furnace or air conditioning unit. High efficiency variable speed gas furnaces and air conditioners offer the best efficiency for standard heating and cooling systems. Variable speed systems will run at lower speeds for longer periods to maintain a temperature at a lower energy consumption.
FACTORS THAT CAN AFFECT ENERGY EFFICIENCY
To ensure your forced air system is running its best, homeowners need to properly maintain their systems. Some factors that lower efficiency include ignoring annual maintenance of fan blades, ductwork, indoor and outdoor coils, and refrigerant levels. Poor ductwork design and quality can also affect how air is distributed throughout the home. To correct these issues, systems require properly sized equipment, additional dampers, and other ductwork modifications to improve airflow to warmer areas of the home.
Another way to improve forced air efficiency is by using a smart thermostat. Smart thermostats automate your home’s temperature, optimizing it for the best efficiency. This can lower the cost of utility bills significantly.
COST SAVINGS WITH FORCED AIR
By combining your system with a smart thermostat and ensuring it is properly maintained, forced air systems can greatly reduce energy bills. If your home already has forced air heat, retrofitting an air conditioning coil and condenser is a low cost way to add centralized air to your entire home.
Ductless Mini-Splits
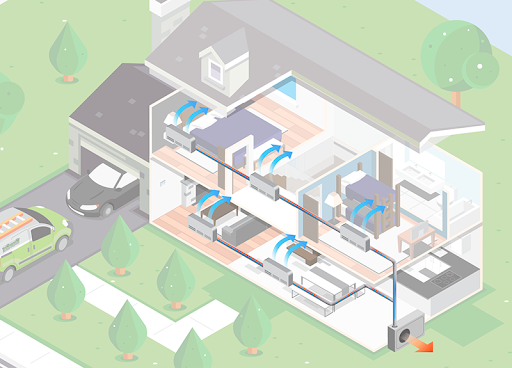
For homes without ductwork, a ductless mini-split system is a great choice for an energy efficient heating and cooling system. Ductless mini-splits are typically wall mounted units but can be ceiling cassettes and wall cassettes on the ground as well. These systems are often used in smaller homes like townhomes, twins, and row homes, but are becoming more applicable to larger homes too. In homes that already have an HVAC system, ductless mini-splits can be utilized in rooms that lack air flow or do not have ductwork, such as attics or sunrooms.
ENERGY EFFICIENCY IN DUCTLESS MINI-SPLITS
Ductless mini-splits are an efficient choice because each individual room can be at a specific temperature. This accommodates rooms that have more sunlight or poor insulation, allowing them to only run when needed. For better control over energy consumption, higher end systems have sensors that detect occupancy and only run when someone is in the room. These systems are controlled via remote control or an app on the customer’s smart phone for easy use.
FACTORS THAT CAN AFFECT ENERGY EFFICIENCY
Since ductless mini-splits are used constantly, their filters need to be cleaned every few weeks to ensure proper efficiency. Homeowners can easily clean the filters themselves though, as they do not require professional maintenance. Ductless mini-splits also need ample space to make sure nothing is blocking air flow. While a clear space is important for air flow, poor location or an oversized unit can also negatively affect efficiency. When properly cared for and installed correctly, ductless mini-splits are a cost-effective choice for heating and cooling.
COST SAVINGS WITH FORCED AIR
Up front, a ductless mini-split has a lower installation cost. Systems can also be sized larger than needed to be able to add additional indoor air handler units. The costs can vary though, depending on sizing of units and additional technology that the homeowner needs or wants. When purchasing a ductless system, manufacturers often offer rebates for extra cost savings. For an additional cost savings on installation, we offer special financing rates for Mitsubishi ductless units.
High Velocity Systems
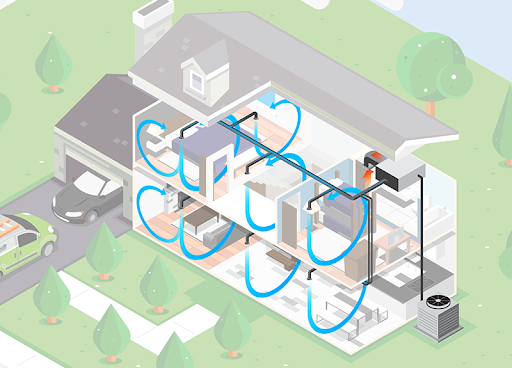
High velocity systems are another choice for an energy efficient air conditioner. While they don’t provide heat, they can be paired with another air source such as a heat pump, geothermal, or hydronic heating system. In a high velocity system, an air handler runs continuously to keep air moving around the home, which reduces the need to constantly turn the system on and off like a traditional air conditioner. To cool the home, air runs through two inch, flexible ductwork that is specifically designed to deliver air quietly at high speeds. With a constant flow of air, high velocity systems help reduce hot spots in rooms and will use less energy over time. High velocity systems, like ductless systems, are ideal for homes without existing ductwork or that don’t allow space for ductwork.
HIGH VELOCITY AS AN ENERGY EFFICIENT AIR CONDITIONER
High Velocity systems are energy efficient air conditioners because they do not need to have the temperatures set as low. They cool more of the home with less energy consumed, as the ductwork is 15% less likely to leak air compared to traditional ducts. Running at a lower air speed allows the system to cool for longer periods of time without using more energy.
FACTORS THAT CAN AFFECT ENERGY EFFICIENCY
While high velocity systems can be an effective way to cool your home, homeowners need to follow proper maintenance to ensure efficiency. High velocity systems require annual inspections and maintenance, along with general cleaning and replacements of air filters. Inadequate returns and filter sizes can also decrease efficiency, as well as improperly sized equipment or ductwork. With adequate maintenance and the right equipment, high velocity is an efficient air conditioner system that can save you money in the long run.
COST SAVINGS WITH HIGH VELOCITY
While a high velocity system is more expensive than traditional air conditioning to install, systems can last up to 20 years, paying for themselves by reducing energy bills. As an energy efficiency system, it consumes less energy because the system does not need to run as much. This greatly lowers utility bills compared to traditional air conditioning systems.
Electric Heat Pumps
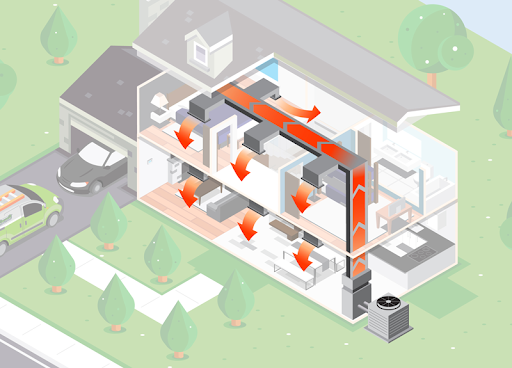
An additional energy efficient system is an electric heat pump. They are a joint heating and cooling system that can come in two types: standard and ductless. Ductless systems are more energy efficient because you can control the temperature from room to room instead of the entire house. However, ducted and ductless systems can be combined to serve whole homes. Just like the mini-split, ductless electric heat pumps can be used in rooms without ductwork or less air flow. Natural gas systems are commonly used for a more efficient home, however for homes that don’t have a direct gas line, an electric heat pump is an alternate choice. They are increasingly being installed to supplement existing heating systems and also add energy efficient air conditioning for ducted solutions.
ENERGY EFFICIENCY
In addition to reducing fossil fuel usage, heat pump systems are efficient because they do not need to generate their own heat or cool air. They draw it in from the outside in order to heat or cool the home. The development of cold climate inverters in recent years has made this option much more practical in the northeast. When paired with an oil unit, high velocity systems improve overall home efficiency by reducing fossil fuel usage. This is a great way to cut costs on oil during the winter.
FACTORS THAT CAN AFFECT ENERGY EFFICIENCY
While electric heat pumps can be used on their own or as a supplement for better efficiency, environmental factors can affect efficiency. By only using electricity, systems can struggle to keep up in extreme temperature conditions. With any air system, annual inspections and proper maintenance is also a must. Energy efficiency can be reduced when the outdoor unit isn’t clean or is covered in debris, when air filters are not replaced, and when seasonal coil cleaning is ignored. When a heat pump system is running at its most efficient, they can save costs over time.
COST SAVINGS WITH ELECTRIC HEAT PUMPS
Electric heat pumps last around 15 years, making installation a worthwhile investment. They can also be connected to solar energy or other renewable power sources for additional efficiency. To incentivise installations even more, utility and manufacturer rebates are frequently available for these systems.
For any home type, an energy efficient system can make a huge difference for the environment and in your wallet. By reducing fossil fuel usage, you can save hundreds of dollars on your yearly utility bills. Just make sure to keep up with proper maintenance to make sure your system runs as efficiently as possible.
Get a full understanding of your heating and cooling options with our HVAC U resources.
Looking to switch to a more energy efficient air conditioner or heater?
Contact us to find the perfect fit for your home.



